Trump’s Import Tariffs: What They Mean for U.S. Jobs and Prices
The Trump administration has significantly expanded import tariffs on foreign goods in 2025, raising taxes on everything from heavy trucks to consumer products imported from countries like Canada, China, India, and members of the EU. These measures are part of a broader trade strategy to protect U.S. industries and boost domestic production — but economists say the effects on jobs and prices are mixed and could create economic challenges for American consumers and businesses. AAJ News+1
📈 Tariffs and Consumer Prices
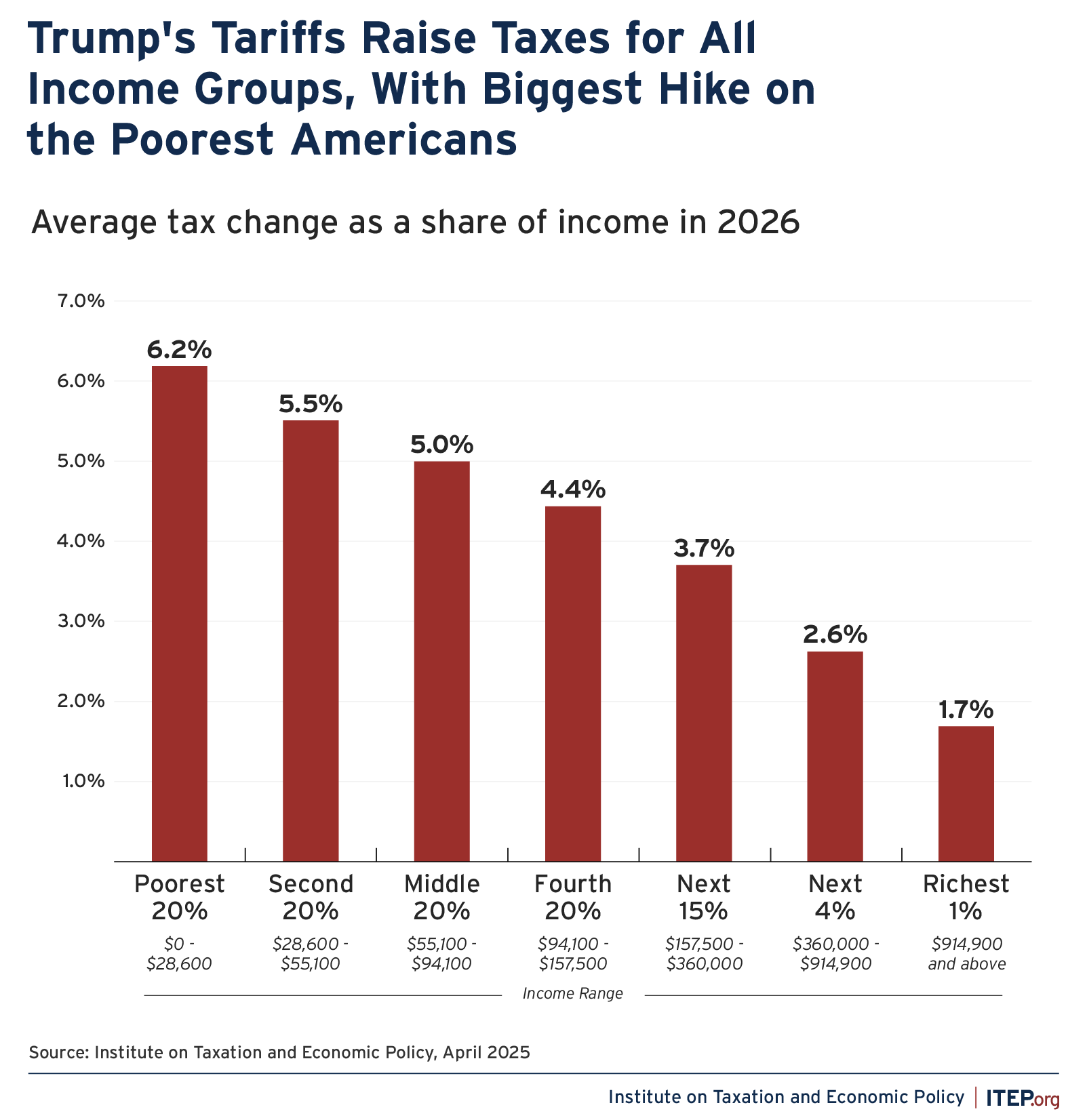
Tariffs are essentially taxes on imported goods, and the cost of these levies is usually passed on to U.S. companies and consumers, leading to higher retail prices. Increased tariffs on products like wine, electronics, and automotive parts have already pushed some retailers to raise prices or stock up before the hikes take full effect in 2026. The Wall Street Journal
According to economic analysts, broad tariffs can lead to higher costs for ordinary Americans, especially on everyday items — a concern echoed in inflation data showing prices remain elevated despite recent slowing. The Guardian
📉 Impact on Jobs and the Labor Market
One of the key arguments from Trump’s trade policy supporters is that tariffs will protect U.S. manufacturing jobs by making foreign goods more expensive compared to American-made products. However, research indicates that the net effect on employment may not be positive:
- Some economists estimate that while tariffs might slightly boost manufacturing jobs, the overall impact on total employment could be negative because higher input costs reduce hiring in other sectors of the economy. Fox Business
- Employers citing tariff-related uncertainty have reported slower hiring or hiring freezes in certain industries, especially where companies depend on imported materials. PBS
In short, while some factory employment might benefit, service industries and businesses that rely on imports might cut jobs or delay expansion, leading to a complex job market impact overall.
🏭 Effects on Business and Global Trade
Trade experts note that tariffs can also prompt retaliatory measures from other countries, making U.S. exports more costly abroad and reducing global demand for American goods. This dynamic can ultimately undermine U.S. competitiveness and put further strain on jobs tied to international trade. Equitable Growth
Moreover, recent changes such as a 25 % tariff on heavy trucks and higher taxes on certain imports reflect Trump’s strategy of trade leverage — pushing foreign companies either to build more products in the U.S. or face significant tax penalties. AAJ News